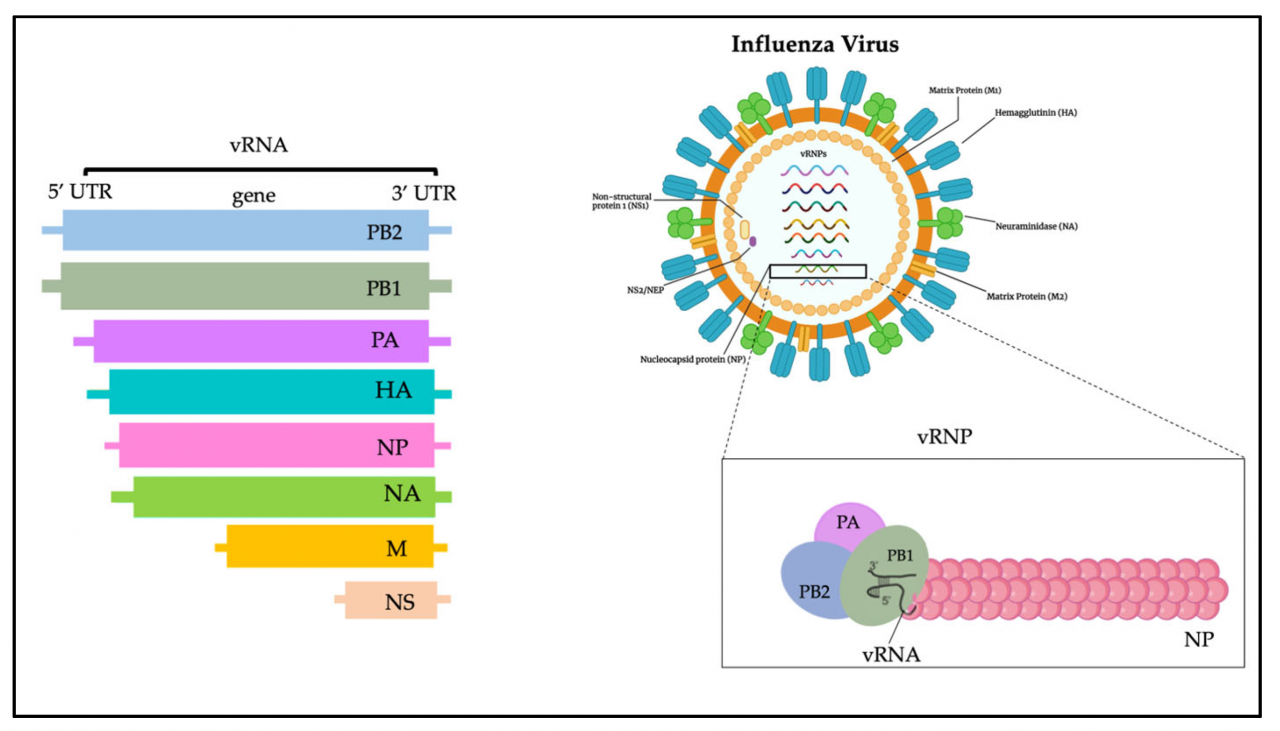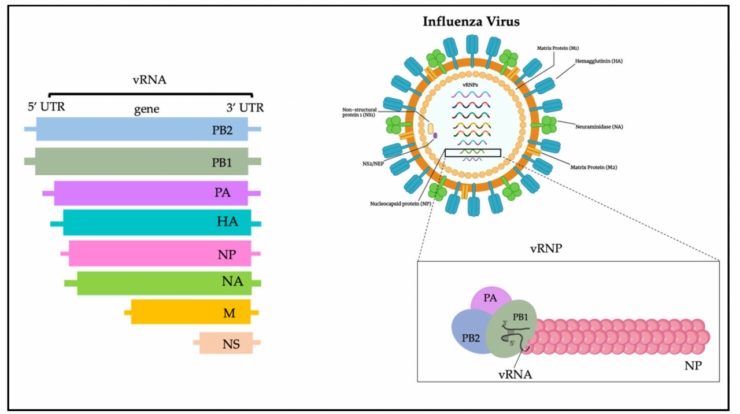
The H5N1 pandemic, a global health crisis, has left an indelible mark on the world. This highly pathogenic avian influenza virus has spread rapidly, causing significant economic and social disruption. Join us as we delve into the complexities of this pandemic, exploring its global impact, symptoms, transmission, prevention, and the ongoing efforts to control its spread.
From its origins in poultry to its potential threat to human health, the H5N1 pandemic has raised concerns worldwide. Understanding the virus and its implications is crucial for mitigating its impact and safeguarding global health.
Global Impact
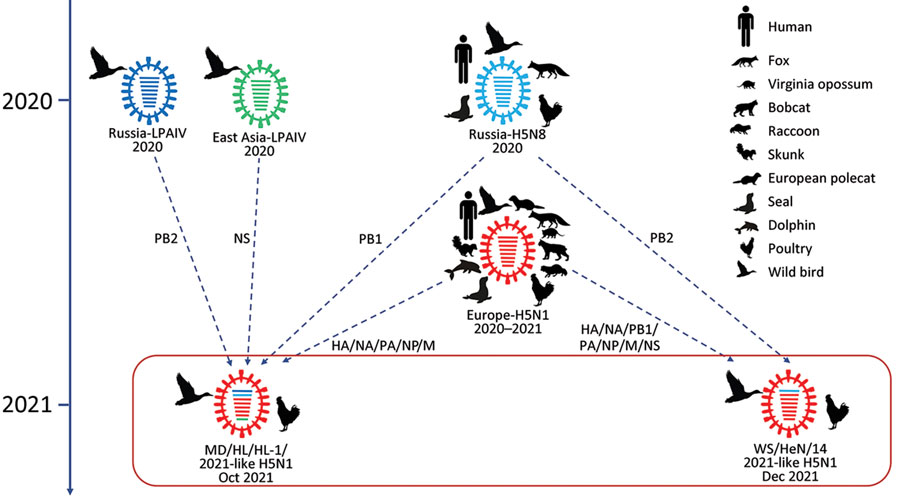
The H5N1 virus has a global distribution, affecting countries across multiple continents. The virus has been detected in poultry and wild birds in Asia, Europe, Africa, and North America.
As of 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) has reported over 860 laboratory-confirmed human cases of H5N1 infection, with a fatality rate of approximately 53%. The majority of cases have occurred in Southeast Asia, with Indonesia, Vietnam, and Cambodia being the most affected countries.
Symptoms and Transmission, H5n1 pandemic
H5N1 infection in humans typically causes severe respiratory illness, with symptoms including fever, cough, sore throat, and muscle aches. In severe cases, the virus can lead to pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and death.
The virus is primarily transmitted from infected birds to humans through direct contact with their bodily fluids or contaminated surfaces. Human-to-human transmission is rare but has been documented in close contacts of infected individuals.
Risk factors for infection include working with poultry or handling infected birds, living in areas with high poultry populations, and traveling to regions where the virus is known to be circulating.
Prevention and Control
Preventing the spread of H5N1 requires a multi-pronged approach involving public health measures, surveillance, and vaccination.
Public health measures include avoiding contact with infected birds, practicing good hygiene, and reporting any suspected cases of infection. Vaccination of poultry is also essential for reducing the risk of transmission to humans.
Antiviral drugs, such as oseltamivir and zanamivir, can be used to treat H5N1 infection and reduce the risk of severe complications.
Economic and Social Impact
The H5N1 pandemic has had a significant economic impact on the poultry industry, leading to the culling of millions of birds and disruptions in trade.
The virus has also had a social impact, causing fear and anxiety among communities and individuals. Travel and trade have been affected, as countries have implemented restrictions to prevent the spread of the virus.
Research and Development
Ongoing research is focused on understanding the evolution of the H5N1 virus, developing new vaccines and antiviral drugs, and improving surveillance and detection methods.
Challenges include the high mutation rate of the virus, the potential for drug resistance, and the need for global collaboration to prevent the spread of the virus.
Public Health Response
Public health organizations play a critical role in responding to the H5N1 pandemic.
They provide guidance on prevention and control measures, conduct surveillance for new cases, and coordinate outbreak investigations.
Challenges faced by public health officials include the lack of a universally effective vaccine, the potential for human-to-human transmission, and the need for international cooperation to prevent the spread of the virus.
Ending Remarks: H5n1 Pandemic
The H5N1 pandemic serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of global health and the importance of preparedness. As research and development continue to unravel the mysteries of this virus, collaboration and vigilance remain essential in combating its threat.
By working together, we can mitigate the impact of future pandemics and safeguard the well-being of our communities.